Exploring the Diverse Modules of SAP ERP
Introduction
SAP ERP is a multifaceted software with various modules, each designed to handle different business processes. These modules are interconnected, ensuring seamless data flow across the enterprise. This article provides an overview of the key SAP ERP modules and their functionalities.
Core Modules of SAP ERP
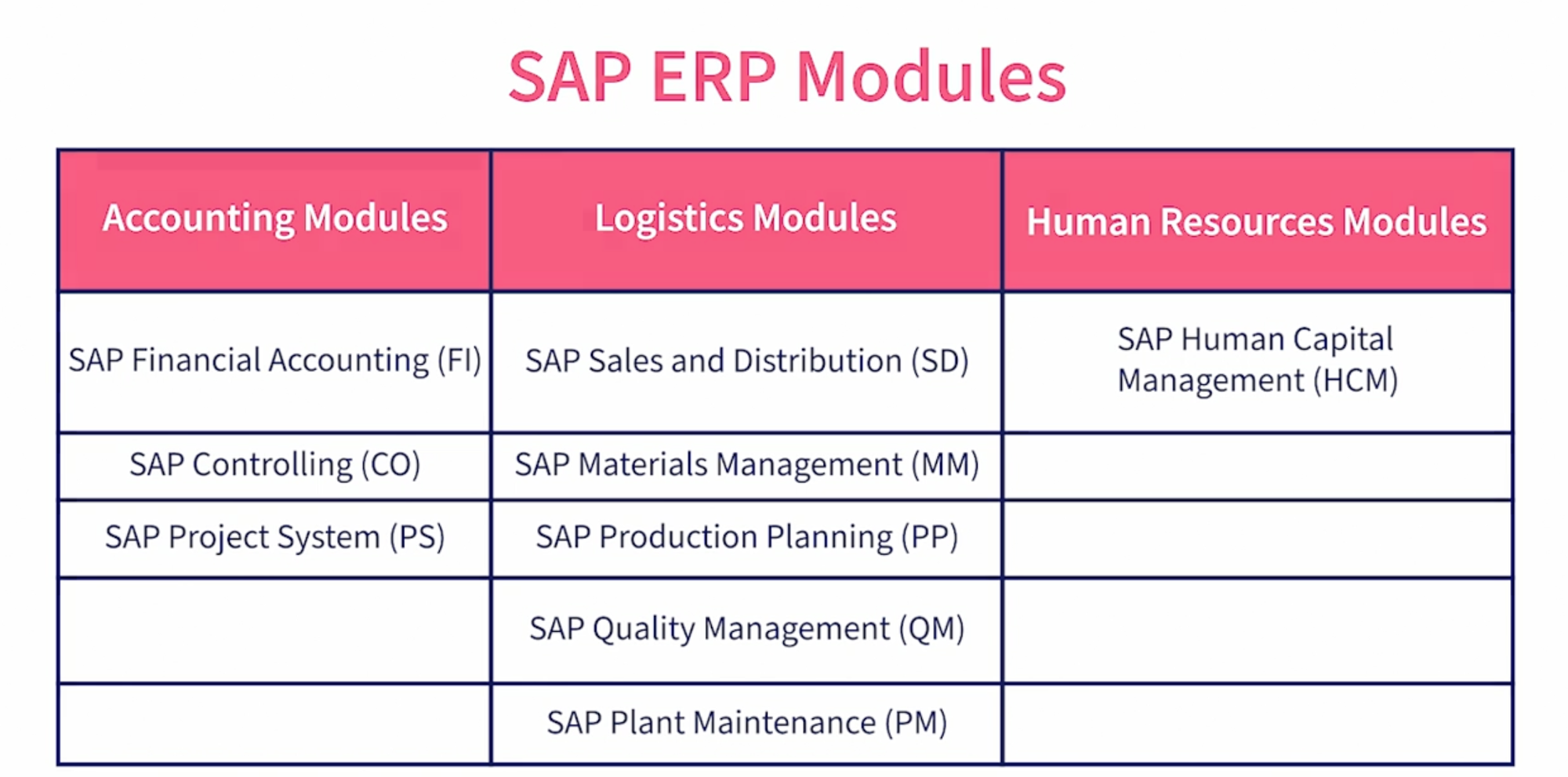
- Financial Accounting (FI): This module manages a company’s financial transactions and reporting requirements. It enables efficient financial accounting and reporting, including ledger management, accounts receivable, and accounts payable.
- Controlling (CO): CO module assists in managing and configuring internal costs. It includes cost element accounting, profit center accounting, and activity-based costing.
- Sales and Distribution (SD): The SD module manages sales and customer distribution data. It encompasses operations like billing, selling, shipping, and transportation of products.
- Material Management (MM): Essential for procurement and inventory management, MM handles material procurement processes, inventory management, and warehouse management.
- Human Capital Management (HCM): This module focuses on HR processes such as personnel administration, payroll, recruitment, and performance management.
- Production Planning (PP): PP module manages production processes, including planning, scheduling, and control of manufacturing activities.
- Plant Maintenance (PM): PM is responsible for maintaining company equipment, ensuring regular and preventive maintenance to reduce the likelihood of unplanned downtimes.
- Quality Management (QM): QM module helps in managing quality in production across the entire process of manufacturing and distribution.
Additional SAP ERP Modules
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): SCM optimizes the supply chain process, including planning, execution, coordination, and collaboration with suppliers.
- Project System (PS): PS module helps in project planning, execution, and monitoring, providing tools for project management.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): CRM focuses on managing and maintaining customer relationships, sales, and marketing activities.
- Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS): This module helps in managing environmental, health, and safety regulations within the enterprise.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): PLM supports the entire lifecycle of a product from conception, through design and manufacture, to service and disposal.
Integration of Modules
- The strength of SAP ERP lies in the integration of these modules, allowing for a unified flow of data across different business functions.
- This integration facilitates comprehensive reporting and analytics, enhancing decision-making processes.
Customization and Flexibility
- While SAP provides these standard modules, they can be customized and scaled according to the business needs.
- Companies can choose the modules relevant to their operations and integrate them with existing systems.
Conclusion
The diverse modules of SAP ERP cover nearly every aspect of business management, making it a robust and versatile tool for organizations. By understanding these modules, businesses can leverage SAP ERP to optimize their processes, improve efficiency, and drive growth. As the business environment evolves, SAP continues to update and expand its modules to meet the ever-changing needs of the business world.